Phased array antennas achieve the purpose of beam scanning by changing the phase and amplitude of the feed of each antenna channel, so they can achieve the purpose of detection, search, identification, tracking and guidance. However, after the antenna design is completed, many important indicators are affected by the inconsistency of the phase and amplitude of each antenna channel, and the initial amplitude phase of each element needs to be calibrated to the same level to achieve better performance. Therefore, phased array calibration technology has become a hot issue in phased array testing, and with the continuous improvement of phased array antenna performance requirements, phased array calibration technology is also constantly developing.
The main calibration methods include near-field scanning measurement method, midfield calibration method, rotation vector method (REV), linear matrix inverse method, mutual coupling calibration method, quadrature coding calibration method, commutation method, etc.
Near-field scanning measurements
Near-field scanning calibration is one of the most commonly used calibration methods for phased arrays, which uses the probe to sample the electric field on the closed surface of the array, and obtains the amplitude phase characteristics and active pattern of the unit through numerical calculation, and then calculates the far-field pattern. Near-field probes are generally 3~5 wavelengths away from phased array antennas.
Midfield calibration
The midfield calibration technology uses the reference antenna to be placed in a specific position in front of the phased array to be measured to test the phased array, and uses these corrected amplitude values to match the antenna unit to achieve the normal operation of the phased array by making a series of corrections to the measured coupling phase value.
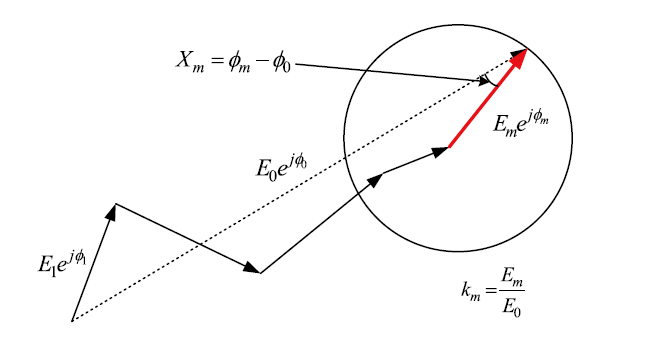
(REV) Rotational Electrical Vector Calibration (REV)
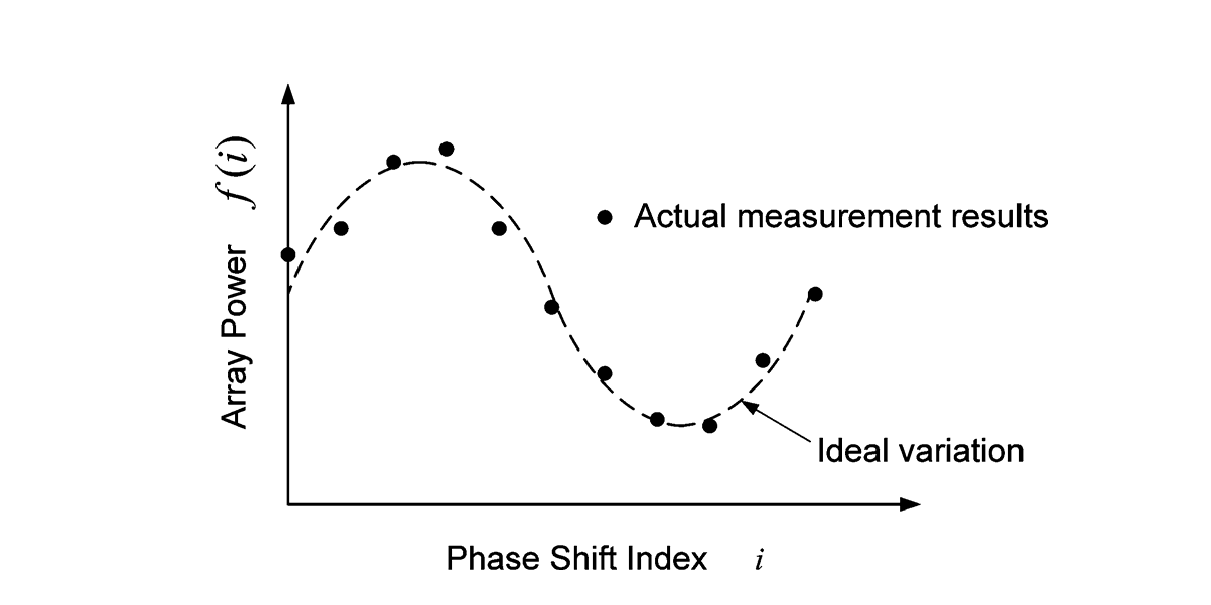
This method is suitable for the occasion that the feed phase of each unit of the array can be regulated by 360°, the process is fixed array other units feed unchanged, according to a certain step to the calibration unit phase 0 ° ~ 360 ° rotation (maximum step value 90 °), and in the far field measurement rotation process to measure the amplitude change of the probe, traverse each unit, and finally solve the amplitude phase error between the elements through post-processing methods such as curve fitting.
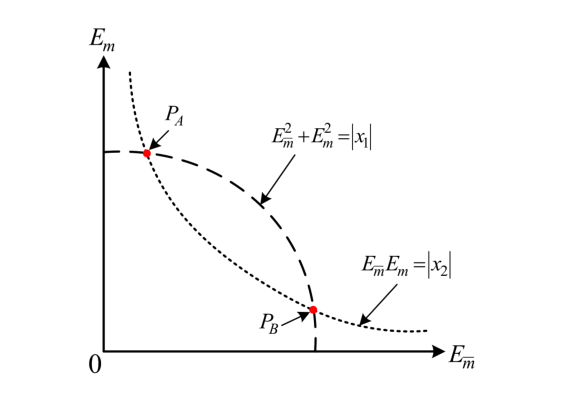
Through the improved rotation vector method, the phase shift value of each element only needs to be reduced to only need to traverse the three states of 0°, 90°, and 180°, and the initial amplitude phase of each element is obtained by solving the equation system for E and E mm , thereby improving the calibration efficiency.
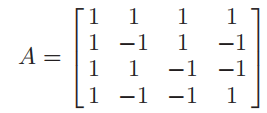
Linear matrix inversion
For the channel consistency measurement of passive array antennas, if it is easier to obtain the phase information of the measurement signal, it is appropriate to use the linear matrix method to reduce the number of measurement states and switching times, and the number of phase shifters is required. The system is based on the single-probe calibration mode, the probe is in the receiving or transmitting state, respectively configured with the preset M group phase configuration state, the link signal amplitude phase is collected, the excitation phase configuration matrix and the system response vector are formed, and finally the channel amplitude phase consistency of the measured array is obtained by solving the linear matrix. The matrix can choose a Hadamard matrix A with condition number 1 to generate a matrix of coefficients of any order.
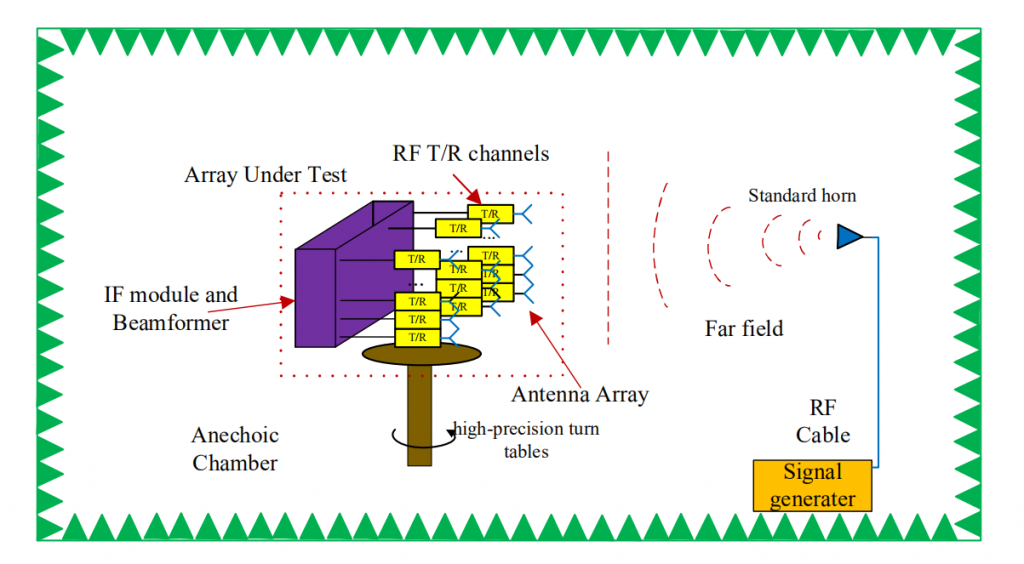
Far-field on/off calibration method
This method can realize the automatic measurement and calibration of the amplitude phase consistency of the array antenna channel in the far field area, the calibration probe system is only composed of a single antenna, the calibration system only needs to control the on-off of the DUT channel, and through N times of data acquisition, the amplitude phase error of the DUT unit with the number of channels N can be reversed by the inversion algorithm.
Mutual coupling calibration method
Mutual Coupling Technology (MCT) and Mutual Coupling Calibration Method (MCCM), as an alternative to external calibration, enable internal in-line calibration of arrays and are therefore considered ideal for calibration in future phased array systems. However, this method requires that the array has a transmit channel and other units can be in the receiving state at the same time, and it is necessary to ensure the consistency of the mutual coupling state between the units and sufficient prior knowledge to assist calibration.
Quadrature coding calibration
The orthogonal encoding calibration algorithm utilizes a time division multiplexing orthogonal encoding signal larger than the number of array units for coherent operation and decoding at the receiving end, greatly reducing the calibration time and N (array) compared to the single antenna calibration method
The number of elements in a column is multiple. By using control circuit orthogonal encoding technology, the array unit can be calibrated using a calibration probe under far-field or near-field conditions, and the phase of the unit can be restored using a coherent receiver and decoder.
Commutation calibration method
The commutation calibration method finally solves the phase amplitude difference of the unit channel by switching the phase of the unit and measuring the change law of the signal, which can realize the unit and system level calibration of phased array radar at the same time.